An Interdisciplinary Study toward Clean Air, Public Health and Sustainable Agriculture: The Case of Crop Residue Burning in North India
HAYASHIDA Sachiko,
RIHN / Nara Women’s UniversityArea : North India
Human health in many developing countries, and especially India, is often threatened by declining air quality. This study tackles the issue of air pollution arising from large-scale burning of rice straw after harvest in the state of Punjab. Burning of rice straw in Punjab has been linked with significant air pollution in Delhi and surrounding regions. To address the problem, we will take an interdisciplinary approach and pursue a pathway of social transformation toward clean air, public health and sustainable agriculture.

A photo of straw burning taken at Ludhiana in the state of Punjab on November 2, 2018.
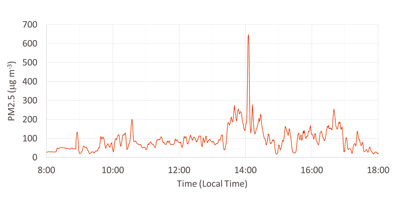
Time series of PM2.5 values that were exposed to the project PI when visiting Punjab on November 2, 2018. The sudden increase of PM2.5 at 14:00 is corresponding to her encounter with a straw burning shown in the Photo 1. Note that the WHO guideline of 24-hours average criterion is 25 μg/m3.
