Study Area
The research activities of Environmental Valuation Project are being conducted in the following
two main field sites.
- Uryu Experimental Forest, Field Science Center for Norhtern Biosphere, Hokkaido
University
- Nara/Wakayama Experimental Forests, Field Science Education and Research
Center, Kyoto University
We set up our main study field for the development of IDEA in
Shumarinai Lake watershed, Hokkaido, Japan. We will investigate the changes in
people's value judgement on this
watershed environment in response to the virtual impact scinarios.
To create the virtual impact scinarios, the project team is collecting natural-scientific
data such as hydrology, material cycling, or tree growth that can be used as
indicators of environmental changes. The members also investigate the sociological
aspects of the local communities through social surveys using interviews, questionnaires,
and focus group sessions.
For IDEA to
be an actual policy-making tool, it is imperative to use realistic environmental
change scenarios that are based on actual environmental monitoring data. To collect
basic data to construct a model to predict long-term ecological changes caused
by the timber management, we are collecting ecological data in wakayama Experimental
Forest where the forests have been managed for long time for timber production.
| Hokkaido University Uryu Experimental Forest |
|
Location: Horokanai-cho, Uryu-gun, Hokkaido, Japan
Uryu Experimental Forest extends 30km over east-west direction and
50km north-south, embracing Shumarinai Lake that is draining
to Uryu River, one of the major tributaries of Ishikari River
system. The forest is located in the coldest region in Japan,
often marking -30 degree C or less (The record minimum was -41.2
deg. C in 1978). The area also has a large snow fall with more
than 2m snow accumulation every year.
The northern part of the Experimental Forest falls in the geological
zone of tertiary andesite bedrock, covered with natural forests of
mixed conifer and deciduous broad-leaf trees, forming a landscape
similar to those in the Eurasian continent. The major tree species
in the mixed forests are, Akaezo spruce (Picea
glehnii), Sakhalin fir (Abies sachaliensis),
Monglian oak (Quercus crispula), birches,
Jaanese elm (Ulmus davidiana var. japonica),
Japanese linden (Tilia japoinca), and
Japanese manchurian ash (Fraxinus mandshurica
var. japonica). Among them, almost pure stands of Mongolian
oak are most commonly found.
The southern part of the forest along Uryu river underlain by serpentine
rocks is covered with monoculture of Akaezo spruce forest (quoted
from the web site of Forest
Research Station, Field Science Center for Northern Biosphere, Hokkaido
University). |

Overview of Shumarinai Lake from the northeast region of Uryu Experimental
Forest |
Jump to: Uryu
Experimental Forest's homepage |
Nara/Wakayama Experimental Forests,
Field Science Education and Research Center, Kyoto University |
|
Experimental Site 1: A private forest in Totsukawa Village, Nara Pref.
Location: Totsukawa Village, Nara Prefecture
Area: Approx. 1000ha
Average annual temperature: 10-11 degree C
Annual precipitation: 2400mm
Elevation: 860-1370m
The watershed encompasses the headwater of Totsukawa River. The underlying
geology is sandy sedimentary rock. The watershed is covered with commercial
cedar forest plantation with 80-year harvesting cycle. The area consists
of 87-year matured plantation forest and 1 to 40-year plantation forests.
Clear-cutting the entire catchment as a management unit maintains the
rows of catchments with single-year stands of different ages (rotational
harvesting).
|

Watersheds juxtaposing to each other have single-aged conifer stands
of different ages |
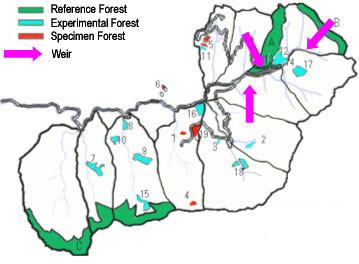
Experimental Site 2: Kyoto University Wakayama Experimental Forest
Area: Approx. 842 ha
Elevation: 455-1,261 m
Annual average temperature: 12.3 degree C
Annual precipitation: 2369mm
Snow depth: <30cm
Potential vegetation: fir, hemlock fir, beech, east asian evergreen
forest. The forest embraces the headwater of Arita River. |
 |
Jump to: Field Science
Education and Research Center's homepage (Japanese only) |
|




